Muscle spasms are involuntary contractions of a muscle, a group of muscles. Often they happen suddenly without any prior warning. Although muscle spasms tend to be harmless and only last a few minutes, they can occasionally be accompanied by sudden sharp bursts of pain causing the sufferer to feel very uncomfortable. Spasmism is when a series of spasms or permanent spasms occur within a muscle or group of muscles. Sometimes muscle spasm can also be cause by certain medical conditions, such as dystonias.
Dystonias is a neurological movement disorder that causes twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures caused through sustained muscle contractions. The dystonia disorder can inherited or birth related. It can also be caused by physical trauma, various poisonings (such as lead poison) infections or even caused by a reaction to drugs like neuroleptics. Neoroleptics are drugs used to treat psychosis, such as conditions like schizophrenia.
Muscle spasms can also occur through sudden contractions of an orifice, this is sometimes related to colic. Colic occurs through spasms in the smooth muscle in particular muscles, such and the throat. This is an episodic pain and can induce nausea and vomiting for the sufferer.
In high stress situations it is thought that muscle spasmcould occur causing a phenomenon known as hysterical strength. Hysterical strength is an unnatural, amazing feat of strength caused by high stress situations, in which a human can summon super human strength. Examples of this happening are often given in stories of mothers gaining the strength to lift a car, with their child trapped underneath, long enough to let them escape.
Although it’s common for people to believe in hysterical strength being caused by bursts of adrenaline there is no medical evidence to support it as these sorts of muscle spasms are created without warning. Also recreating the situation in which this occurs would be unethical and dangerous. Muscle spasms often occur soon after muscle injuries. Initially when the spasm occurs the muscle will be tight, at this point it is very important to ensure treatment so that a muscle knot does not form.
Muscle knots tend to form after two weeks of muscle spasm and are very painful, so it is advised that the initial spasm be treated before it turns to a knot. There are numerous treatments for muscle spasms to stop them knotting such as, massage therapy, electrical stimulation or trigger point injections. However spasm can be treated early on with products such as the painwave x4000 to help prevent the occurrence of knots in the muscle. This sort of treatment uses bioelectromagnets and is completely pain free. These sorts of treatments are especially ideal for people allergic to specific medical drugs, or if you just prefer a natural method of pain relief.
Treatments such as bio electromagnets are available through searching on the Internet and should you have any questions about injuries it is recommended you speak either to your doctor or a medical sales assistant and they should be able to provide advice specific to you to help in the best way possible. Always be sure to get serious injuries checked by a health professional before undertaking any sort of treatment.
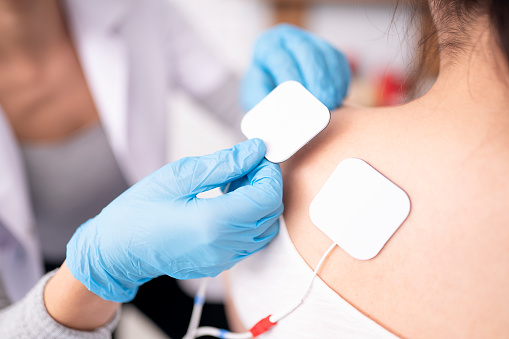
Muscle stims, short for muscle electrical stimulation, is a technique used to contract and relax muscles by applying electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the skin near the affected muscle or muscle group. It is also known as electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) therapy or neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES). The therapy is used to relieve pain, improve muscle strength and endurance, and promote healing in conditions such as muscle strains, sprains, and injuries. It can also be used to improve athletic performance and as a form of physical therapy or as an adjunct to other types of therapy.
Muscle stims have been used for centuries, with the ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all using forms of electrical therapy to treat a variety of ailments. However, it wasn’t until the late 19th century that muscle stims began to be used for muscle stimulation. In the 1920s and 1930s, a Russian physiologist named Dr. Vladimir Marek began using muscle stims to treat muscle weakness and paralysis. By the 1950s, muscle stims had become a popular treatment in Europe and the United States for a variety of conditions, including muscle pain and weakness, spinal cord injuries, and paralysis.
Muscle stims work by delivering electrical impulses to the muscles through electrodes placed on the skin near the affected muscle or muscle group. These impulses cause the muscle to contract and relax, which can help to relieve pain, improve muscle strength and endurance, and promote healing. The intensity of the impulses can be adjusted to suit the individual needs of the patient, and the therapy can be used to target specific muscle groups or to stimulate the entire body.
The electrical impulses are delivered in a pattern that mimics the way the brain sends signals to the muscles to contract naturally, this is called Interferential Current (IFC) or High-Frequency electrical stimulation. This pattern of electrical stimulation has been shown to be effective in recruiting muscle fibers, which can help to improve muscle strength and endurance.
Muscle stims are used to treat a variety of conditions including muscle pain and weakness, spinal cord injuries, and paralysis. It is also used to improve athletic performance, and may be used as a form of physical therapy or as an adjunct to other types of therapy. It has been used to help people with a number of conditions such as chronic pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, and muscle spasms. Muscle stims are also used to improve muscle strength and endurance in people who have conditions that cause muscle weakness, such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and certain types of muscular dystrophy. It is also used to help people with certain types of paralysis, such as spinal cord injuries and stroke, to regain muscle function.
Athletic Performance
Muscle stims have been used to improve athletic performance by increasing muscle strength and endurance. It is also used to help athletes recover from injuries, such as muscle strains and sprains. The electrical impulses delivered during muscle stims can help to increase blood flow to the muscles, which can help to speed up the healing process.
Physical Therapy
Muscle stims are often used as a form of physical therapy to help people recover from injuries, such as muscle strains and sprains. The therapy can help to relieve pain, improve muscle strength and endurance, and promote healing. Physical therapists may use muscle stims as an adjunct to other forms of therapy, such as exercises and stretching.
Safety
Muscle stims are generally considered safe, but as with any treatment, there are some potential risks and side effects.
Treating Depression With Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
First of all, to discuss how Treating Depression with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression, we need to define exactly what it is. TMS is a ground breaking technique that uses electromagnetic fields to stimulate the brain in ways that mimic the effect of antidepressants by acting like a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and increasing extracellular serotonin concentrations in the brain. This is an experimental application of an FDA approved machine. TMS works by positioning the TMS machine over the cranium to transmit short, focused magnetic pulses through the skull where an electrical current is induced in the brain tissue. Unlike electroconvulsive therapy that causes seizures and requires the administration of a sedative, the TMS method is done without sedation and does not cause the major seizures. This is because TMS can target a very small region. At the beginning of each treatment, a health care professional will place the magnet over the head of the patient and proceed to find the motor threshold of the patient. This threshold is defined as the point at which the electrical current is sufficient to make the finger of the patient twitch. This threshold will vary from patient to patient and session to session.
TMS is a better alternative for patients who cannot tolerate antidepressants due to the side effects. This method of treatment has been approved in Canada and Israel for the treatment of major depression in patients not responding to more traditional therapies. This technique has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States yet. For those who have exhausted all other treatment options, this appears to be the choice with the least amount of dangerous side effects. Some of the common side effects to this procedure are headaches, scalp pain at the site of the stimulation, dizziness, facial muscle spasms, and hearing problems. Some of the rare adverse reactions are seizures and mania. Long term effects of this procedure are unknown at this time.
Here is a simplified version of what is going on when functional restoration electrotherapy is used in both of the above situations.
The natural movement in our body is to enlist the smaller diameter muscle fibers first, followed by recruiting the larger diameter muscle fibers last. The coordinated recruitment provides us with a smooth movement, not a jerky nonfunctioning movement. With the use of functional electrical stimulation we do the exact opposite. With external sources of electricity the first fibers to fire are the larger diameter fibers. If the electrical current from the electric stimulation machine is high then after recruiting the larger diameter motor nerves then the smaller diameter nerves are recruited. The effect is to have more motor fibers recruited using functional stimulation and volitional exercises than one would have with solely volitional exercising.