Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) is a relatively common inflammatory disorder that primarily affects older adults, usually those over the age of 50. It is characterized by muscle pain and stiffness, primarily in the shoulders, neck, hips, and thighs. PMR is often associated with another condition called giant cell arteritis (GCA), which involves inflammation of the blood vessels, particularly those in the head. Here’s an in-depth explanation of Polymyalgia Rheumatica and its impact on patients:
1. Symptoms:
• Muscle Pain and Stiffness: The hallmark symptom of PMR is widespread pain and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This can severely limit movement and affect daily activities.
• Fatigue: Patients with PMR often experience significant fatigue and a lack of energy.
• Reduced Range of Motion: The stiffness can lead to reduced range of motion in the affected joints.
• Weakness: Muscular weakness can be experienced, especially when trying to lift objects or perform repetitive movements.
• Fever and Weight Loss: Some patients may also experience mild fever and unintentional weight loss.
2. Diagnosis:
• The diagnosis of PMR is primarily based on the patient’s clinical presentation, symptoms, and the exclusion of other conditions.
• Blood tests, such as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level, are often elevated in PMR due to the inflammatory nature of the condition.
• Imaging studies like ultrasound and MRI may help confirm the diagnosis and exclude other causes of pain.
3. Causes and Risk Factors:
• The exact cause of PMR is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve an autoimmune response, where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
• Genetic predisposition and environmental factors may play a role.
4. Impact on Patients:
• PMR can have a significant impact on patients’ quality of life due to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
• Daily activities, including getting dressed, combing hair, and lifting objects, can become challenging.
• Fatigue and discomfort may lead to social withdrawal and reduced participation in activities.
5. Treatment:
• The primary treatment for PMR is corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, which help to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
• Corticosteroids are typically effective, but long-term use can have side effects, including osteoporosis, weight gain, and increased risk of infections.
• The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and minimize potential complications.
6. Prognosis:
• With appropriate treatment, most patients experience significant improvement in symptoms within a few weeks to months.
• Gradual tapering of corticosteroid dosage is often recommended to minimize side effects.
• PMR can recur, and some patients may require ongoing low-dose corticosteroid treatment.
7. Relationship with Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA):
• Around 15-30% of patients with PMR also develop GCA, a condition characterized by inflammation of blood vessels, particularly those in the head.
• GCA can lead to severe complications, including vision loss, if not treated promptly.
• Both PMR and GCA often respond to corticosteroid treatment.
8. Management and Lifestyle:
• Gentle exercises and stretching can help improve mobility and reduce stiffness.
• Adequate rest and a balanced diet are important for managing fatigue and supporting overall health.
• Regular medical follow-up is essential to monitor response to treatment and manage potential complications.
In conclusion, Polymyalgia Rheumatica is a condition characterized by muscle pain, stiffness, and fatigue primarily affecting older adults. While its exact cause remains unclear, corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment, helping patients manage symptoms and regain functional abilities. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial to improve the quality of life for individuals living with PMR.
Low-dose prednisone refers to the use of the corticosteroid medication prednisone at lower doses than typically prescribed for more severe inflammatory conditions. Prednisone is a synthetic corticosteroid that mimics the effects of cortisol, a natural hormone produced by the adrenal glands. It has potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, making it effective for treating various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Here’s an in-depth explanation of low-dose prednisone:
1. Corticosteroids and Inflammation:
• Corticosteroids like prednisone work by suppressing the immune system’s inflammatory response. They inhibit the production of substances that cause inflammation and immune activity.
• In higher doses, corticosteroids are used to treat conditions like severe asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
2. Low-Dose Prednisone:
• Low-dose prednisone involves using the medication at doses significantly lower than the doses prescribed for acute or severe inflammation.
• The goal is to provide symptom relief and disease management while minimizing the risk of potential side effects associated with high doses.
3. Conditions Treated with Low-Dose Prednisone:
• Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Low-dose prednisone is often used to manage chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis).
• Autoimmune Disorders: It can help suppress the immune response in autoimmune disorders where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
• Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Low-dose prednisone may be used to manage exacerbations in individuals with severe COPD.
• Allergic Reactions: It can be prescribed for severe allergic reactions or asthma exacerbations.
4. Benefits of Low-Dose Prednisone:
• Inflammation Control: Even at low doses, prednisone effectively reduces inflammation, alleviating pain, swelling, and discomfort.
• Symptom Management: Low-dose prednisone helps manage symptoms and maintain functional abilities in chronic conditions.
• Preventing Flares: It can prevent disease flares in chronic conditions prone to periodic exacerbations.
5. Risks and Side Effects:
• Minimized Side Effects: At low doses, the risk of serious side effects associated with high-dose prednisone is reduced. However, some side effects may still occur.
• Bone Health: Long-term use of prednisone, even at low doses, can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
• Adrenal Suppression: Prolonged use of any dose of prednisone can suppress the adrenal glands’ natural cortisol production, potentially affecting the body’s response to stress.
• Immune Suppression: Low-dose prednisone can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
6. Monitoring and Management:
• Regular medical monitoring is essential when using low-dose prednisone to assess its effectiveness and monitor for potential side effects.
• Calcium and vitamin D supplementation may be recommended to support bone health.
• Adrenal function should be assessed periodically, especially if the medication is used long-term.
7. Individualization of Treatment:
• The decision to use low-dose prednisone is made on an individual basis, considering the specific condition, its severity, the patient’s overall health, and potential risks and benefits.
• Patients should be informed about the potential benefits and risks of using corticosteroids.
In conclusion, low-dose prednisone is a treatment strategy that involves using the corticosteroid medication at lower doses to manage chronic inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. While it provides symptom relief and disease control, it’s important to weigh the benefits against the potential risks and side effects. Close medical supervision is crucial to ensure optimal management and minimize any adverse effects.
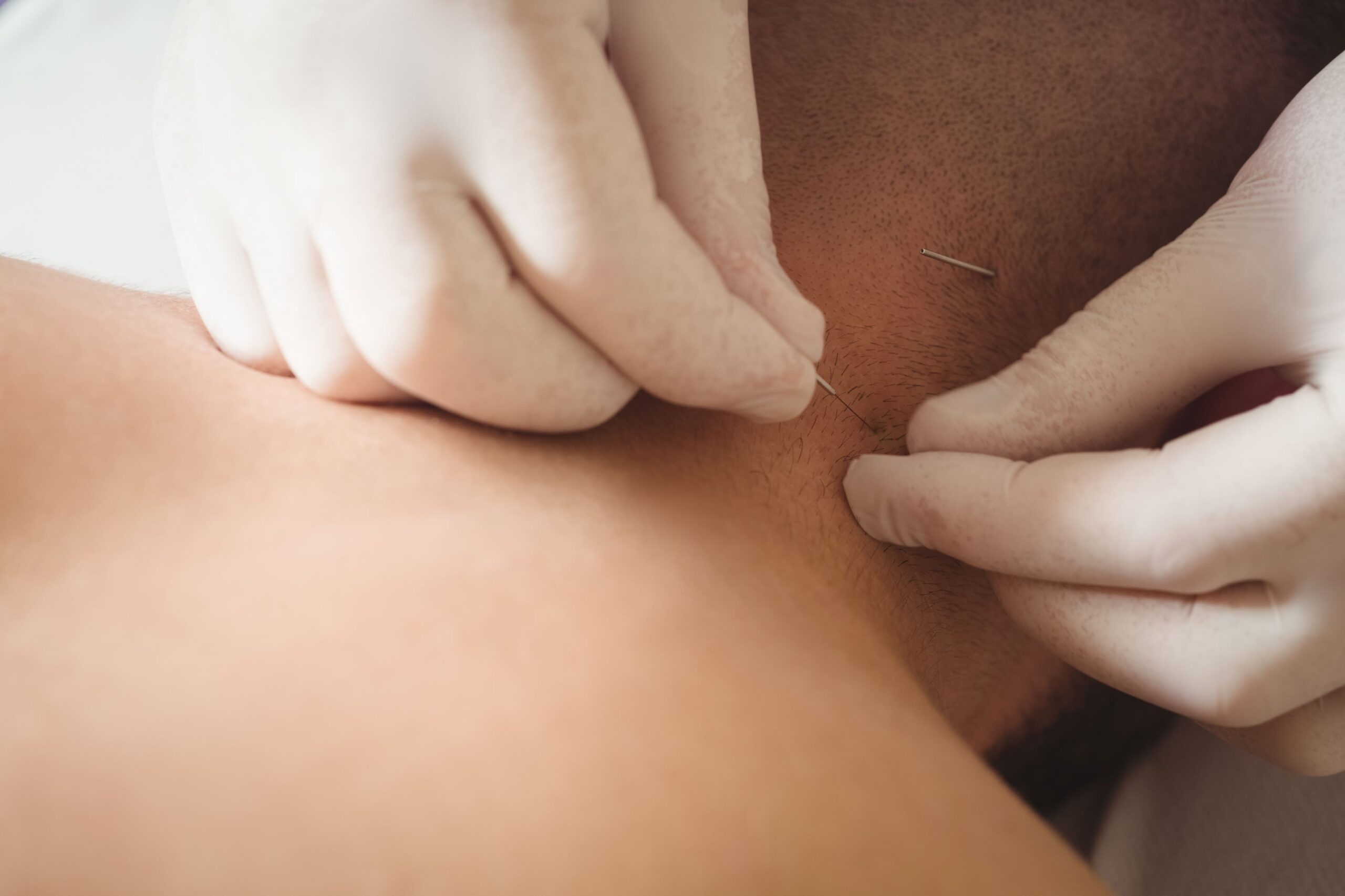
Acupuncture is an alternative therapeutic approach that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy pathways and promote natural healing. When combined with low-dose prednisone treatment, acupuncture can offer several potential benefits for individuals with Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) who are dealing with chronic pain. Here are the benefits of using acupuncture in conjunction with low-dose prednisone for managing chronic pain in PMR patients:
1. Enhanced Pain Relief:
• Acupuncture has been shown to stimulate the release of endorphins and other natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body.
• When used alongside low-dose prednisone, acupuncture may amplify the pain-relief effects, reducing discomfort and enhancing overall pain management.
2. Reduced Dependence on Medication:
• Acupuncture can potentially help decrease the reliance on pain medications, including prednisone, by providing an alternative method for managing pain.
• This may be particularly beneficial for individuals who want to minimize medication side effects or gradually reduce their dosage.
3. Improved Muscle Function:
• Acupuncture’s influence on blood circulation and muscle relaxation can lead to improved muscle function and reduced stiffness.
• For PMR patients, this can mean increased mobility and ease in performing daily activities.
4. Stress Reduction and Relaxation:
• Acupuncture is known to promote relaxation and reduce stress by stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system.
• For PMR patients, who often experience physical and emotional stress due to chronic pain, acupuncture can contribute to a better sense of well-being.
5. Enhanced Sleep Quality:
• Chronic pain can disrupt sleep patterns. Acupuncture’s calming effects may help improve sleep quality by reducing pain-related disturbances.
6. Tailored Treatment Approach:
• Acupuncture treatments are individualized based on the patient’s unique symptoms and needs.
• PMR patients receiving low-dose prednisone may benefit from acupuncture sessions specifically tailored to address their pain areas and overall health condition.
7. Holistic Approach:
• Acupuncture takes a holistic approach to health, considering both physical and emotional aspects of well-being.
• This complements the holistic approach often used in managing chronic conditions like PMR, which can affect multiple dimensions of a patient’s life.
8. Minimal Side Effects:
• Acupuncture is generally considered safe when performed by a trained and qualified practitioner.
• Compared to certain medications, acupuncture carries minimal risk of adverse effects or interactions, making it a viable option for individuals already on low-dose prednisone.
9. Potential Long-Term Benefits:
• Consistent acupuncture sessions may lead to cumulative benefits over time, contributing to sustainable pain relief and improved quality of life for PMR patients.
10. Integrative Approach:
• Acupuncture can be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes low-dose prednisone, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
• Combining different modalities can address pain from multiple angles and offer a more holistic solution.
Note: While acupuncture can offer several potential benefits, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating it into your treatment regimen, especially when taking medication like low-dose prednisone. A qualified acupuncturist should be selected, and open communication between the patient, their rheumatologist, and acupuncturist is essential to ensure safe and effective care.
In conclusion, combining acupuncture with low-dose prednisone treatment for chronic pain management in Polymyalgia Rheumatica patients can provide a holistic and complementary approach. By leveraging acupuncture’s potential pain-relieving effects, individuals may experience improved pain management, enhanced muscle function, reduced stress, and an overall better quality of life while undergoing low-dose prednisone treatment.